Introduction to Graph Databases
- 1. Introduction to Graph Databases Chicago Graph Database Meet-Up Max De Marzi
- 2. About Me Built the Neography Gem (Ruby Wrapper to the Neo4j REST API) Playing with Neo4j since 10/2009 • My Blog: http://maxdemarzi.com • Find me on Twitter: @maxdemarzi • Email me: maxdemarzi@gmail.com • GitHub: http://github.com/maxdemarzi
- 3. Agenda • Trends in Data • NOSQL • What is a Graph? • What is a Graph Database? • What is Neo4j?
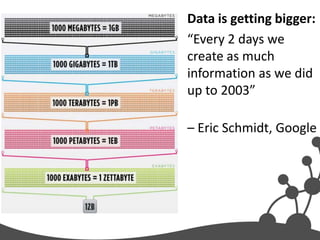
- 5. Data is getting bigger: “Every 2 days we create as much information as we did up to 2003” – Eric Schmidt, Google
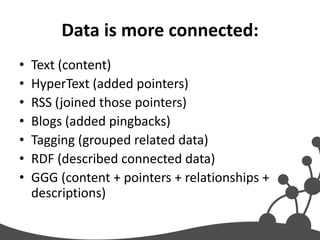
- 6. Data is more connected: • Text (content) • HyperText (added pointers) • RSS (joined those pointers) • Blogs (added pingbacks) • Tagging (grouped related data) • RDF (described connected data) • GGG (content + pointers + relationships + descriptions)
- 7. Data is more Semi-Structured: • If you tried to collect all the data of every movie ever made, how would you model it? • Actors, Characters, Locations, Dates, Costs, Ratings, Showings, Ticket Sales, etc.
- 9. Less than 10% of the NOSQL Vendors
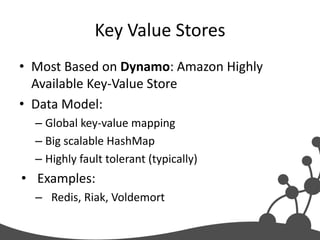
- 10. Key Value Stores • Most Based on Dynamo: Amazon Highly Available Key-Value Store • Data Model: – Global key-value mapping – Big scalable HashMap – Highly fault tolerant (typically) • Examples: – Redis, Riak, Voldemort
- 11. Key Value Stores: Pros and Cons • Pros: – Simple data model – Scalable • Cons – Create your own “foreign keys” – Poor for complex data
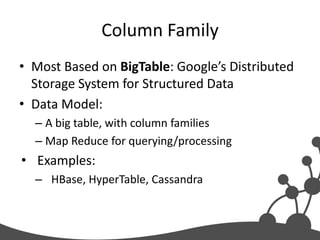
- 12. Column Family • Most Based on BigTable: Google’s Distributed Storage System for Structured Data • Data Model: – A big table, with column families – Map Reduce for querying/processing • Examples: – HBase, HyperTable, Cassandra
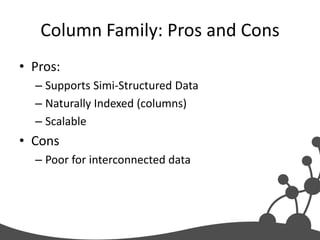
- 13. Column Family: Pros and Cons • Pros: – Supports Simi-Structured Data – Naturally Indexed (columns) – Scalable • Cons – Poor for interconnected data
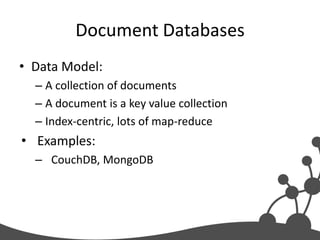
- 14. Document Databases • Data Model: – A collection of documents – A document is a key value collection – Index-centric, lots of map-reduce • Examples: – CouchDB, MongoDB
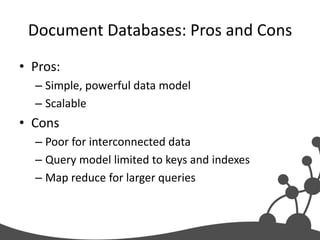
- 15. Document Databases: Pros and Cons • Pros: – Simple, powerful data model – Scalable • Cons – Poor for interconnected data – Query model limited to keys and indexes – Map reduce for larger queries
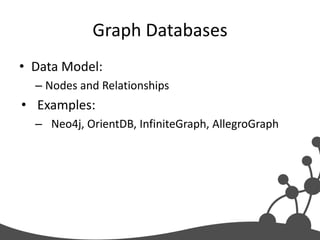
- 16. Graph Databases • Data Model: – Nodes and Relationships • Examples: – Neo4j, OrientDB, InfiniteGraph, AllegroGraph
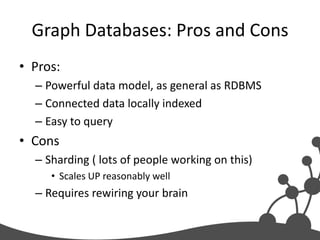
- 17. Graph Databases: Pros and Cons • Pros: – Powerful data model, as general as RDBMS – Connected data locally indexed – Easy to query • Cons – Sharding ( lots of people working on this) • Scales UP reasonably well – Requires rewiring your brain
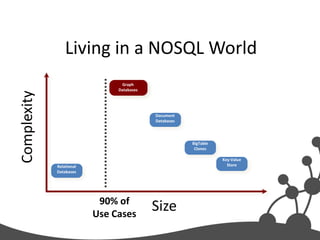
- 18. Living in a NOSQL World RDBMS Graph Databases Complexity Document Databases BigTable Clones Key-Value Relational Store Databases 90% of Use Cases Size
- 19. What is a Graph?
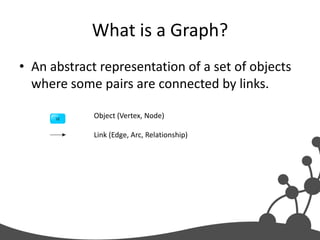
- 20. What is a Graph? • An abstract representation of a set of objects where some pairs are connected by links. Object (Vertex, Node) Link (Edge, Arc, Relationship)
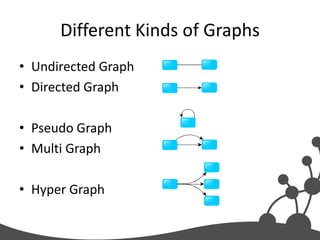
- 21. Different Kinds of Graphs • Undirected Graph • Directed Graph • Pseudo Graph • Multi Graph • Hyper Graph
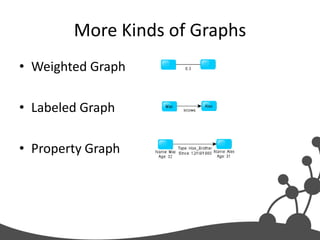
- 22. More Kinds of Graphs • Weighted Graph • Labeled Graph • Property Graph
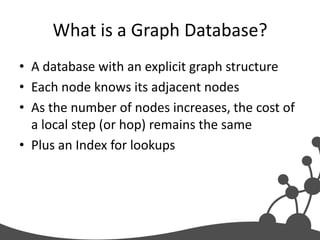
- 23. What is a Graph Database? • A database with an explicit graph structure • Each node knows its adjacent nodes • As the number of nodes increases, the cost of a local step (or hop) remains the same • Plus an Index for lookups
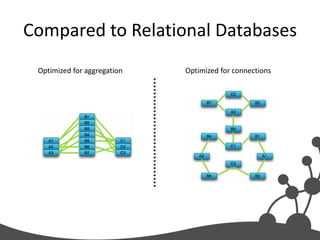
- 24. Compared to Relational Databases Optimized for aggregation Optimized for connections
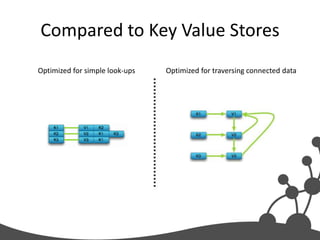
- 25. Compared to Key Value Stores Optimized for simple look-ups Optimized for traversing connected data
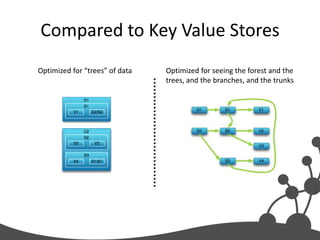
- 26. Compared to Key Value Stores Optimized for “trees” of data Optimized for seeing the forest and the trees, and the branches, and the trunks
- 27. What is Neo4j?
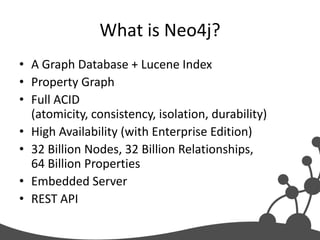
- 28. What is Neo4j? • A Graph Database + Lucene Index • Property Graph • Full ACID (atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) • High Availability (with Enterprise Edition) • 32 Billion Nodes, 32 Billion Relationships, 64 Billion Properties • Embedded Server • REST API
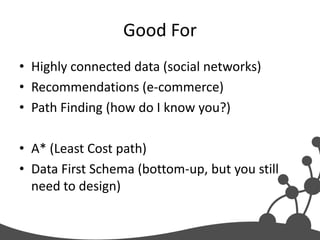
- 29. Good For • Highly connected data (social networks) • Recommendations (e-commerce) • Path Finding (how do I know you?) • A* (Least Cost path) • Data First Schema (bottom-up, but you still need to design)
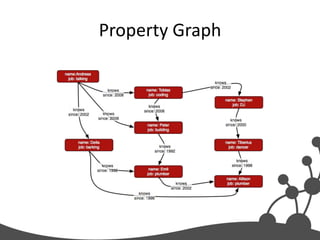
- 30. Property Graph
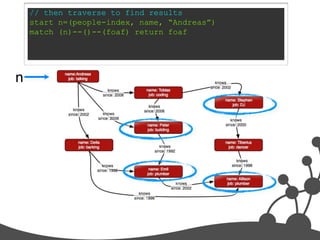
- 31. // then traverse to find results start n=(people-index, name, “Andreas”) match (n)--()--(foaf) return foaf n
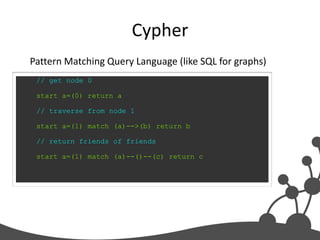
- 32. Cypher Pattern Matching Query Language (like SQL for graphs) // get node 0 start a=(0) return a // traverse from node 1 start a=(1) match (a)-->(b) return b // return friends of friends start a=(1) match (a)--()--(c) return c
- 33. Gremlin A Graph Scripting DSL (groovy-based) // get node 0 g.v(0) // nodes with incoming relationship g.v(0).in // outgoing “KNOWS” relationship g.v(0).out(“KNOWS”)
- 34. If you’ve ever • Joined more than 7 tables together • Modeled a graph in a table • Written a recursive CTE • Tried to write some crazy stored procedure with multiple recursive self and inner joins You should use Neo4j
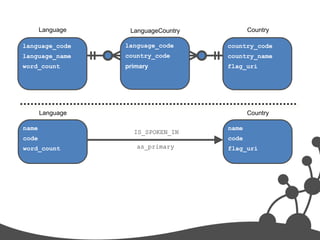
- 35. Language LanguageCountry Country language_code language_code country_code language_name country_code country_name word_count primary flag_uri Language Country name name IS_SPOKEN_IN code code word_count as_primary flag_uri
- 36. name: “Canada” languages_spoken: “[ „English‟, „French‟ ]” language:“English” spoken_in name: “USA” name: “Canada” language:“French” spoken_in name: “France”
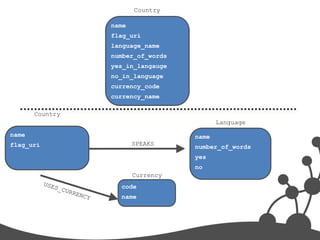
- 37. Country name flag_uri language_name number_of_words yes_in_langauge no_in_language currency_code currency_name Country Language name name flag_uri SPEAKS number_of_words yes no Currency code name
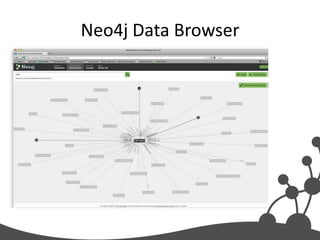
- 39. Neo4j Console
- 40. console.neo4j.org Try it right now: start n=node(*) match n-[r:LOVES]->m return n, type(r), m Notice the two nodes in red, they are your result set.
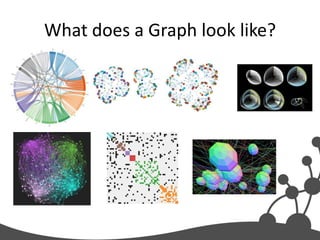
- 41. What does a Graph look like?
- 42. Questions? ?
Editor's Notes
- #22: An undirected graph is one in which edges have no orientation. The edge (a, b) is identical to the edge (b, a).A directed graph or digraph is an ordered pair D = (V, A)A pseudo graph is a graph with loopsA multi graph allows for multiple edges between nodesA hyper graph allows an edge to join more than two nodes
- #23: A weighted graph has a number assigned to each edgeAlabeled graph has a label assigned to each node or edgeA property graph has keys and values for each node or edge
- #29: Atomic = all or nothing, consistent = stay consistent from one tx to another, isolation = no tx will mess with another tx, durability = once tx committed, it stays












![name: “Canada”
languages_spoken: “[ „English‟, „French‟ ]”
language:“English” spoken_in
name: “USA”
name: “Canada”
language:“French” spoken_in
name: “France”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beginnerpresentation-120429104540-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-Graph-Databases-36-320.jpg)
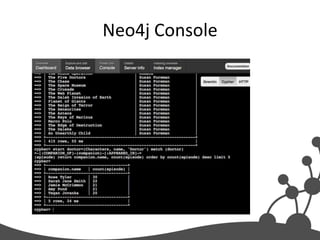
![console.neo4j.org
Try it right now:
start n=node(*) match n-[r:LOVES]->m return n, type(r), m
Notice the two nodes in red, they are your result set.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beginnerpresentation-120429104540-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-Graph-Databases-40-320.jpg)