NoSQL and MapReduce
- 1. NoSQL databases and MapReduceJ SinghEarly Stage IT
- 2. What’s so fun about databases?Traditional database discussions talked aboutEmployee recordsBank recordsNow we talk aboutWeb searchData miningThe collective intelligence of tweetsScientific and medical databases
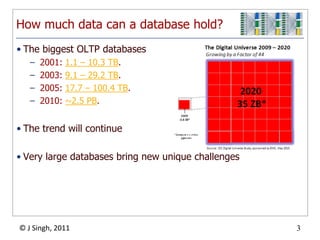
- 3. How much data can a database hold?The biggest OLTP databases2001: 1.1 – 10.3 TB.2003: 9.1 – 29.2 TB.2005: 17.7 – 100.4 TB.2010: ~2.5 PB.The trend will continueVery large databases bring new unique challenges
- 4. Historical ContextLate 1990’s.The web scales out.Suddenly, databases not adequate for holding the data being accumulatedScale out vs. Scale up
- 5. Brewer’s Conjecture (p1)Source: Eric Brewer’s July 2000 PODC KeynoteMain points:Classic “Distributed Systems” don’t workThey focus on computation, not dataDistributing computation is easy, distributing data is hardDBMS research is about ACID (mostly)Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation and DurabilityBut we forfeit “C” and “I” for availability, graceful degradation and performance – this tradeoff is fundamentalBASEBasically AvailableSoft-stateEventual Consistency
- 6. Brewer’s Conjecture (p2)BASEWeak consistencystale data OKAvailability firstBest effortApproximate answers OKAggressive (optimistic)Simpler!FasterEasier evolutionACIDStrong consistencyIsolationFocus on “commit”Nested transactionsAvailability?Conservative (pessimistic)Difficult evolution (e.g. schema)But I think it’s a spectrumEric Brewer
- 7. CAP TheoremSince then,Brewer’s conjecture formally proved: Gilbert & Lynch, 2002Thus Brewer’s conjecture became the CAP theorem……and contributed to the birth of the NoSQL movementBut the theory is not settledWhile http://nosql-database.org/ lists 122 NoSQL databases
- 8. What is NoSQL?Stands for Not Only SQLClass of non-relational data storage systemsUsually do not require a fixed table schema nor do they use the concept of joinsAll NoSQL offerings relax one or more of the ACID properties
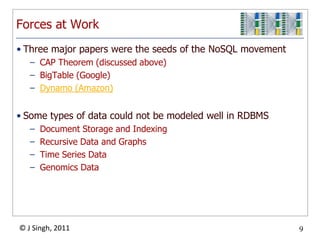
- 9. Forces at WorkThree major papers were the seeds of the NoSQL movementCAP Theorem (discussed above)BigTable(Google)Dynamo (Amazon)Some types of data could not be modeled well in RDBMSDocument Storage and IndexingRecursive Data and GraphsTime Series DataGenomics Data
- 10. NoSQL DatabasesKey-Value StoresA storage system that stores values, indexed by a key.Example: Voldemort, Dynomite, Tokyo CabinetBigTable Clones (aka "ColumnFamily")A tabular model where each row (at least in theory) can have an individual configuration of columns.Example: HBase, Hypertable, Cassandra, Amazon SimpleDB
- 11. NoSQL DatabasesDocument DatabasesCollections of documents, which contain key-value collections (called "documents")Example: CouchDB, MongoDB, RiakGraph DatabasesNodes & relationships, both of which can hold key-value pairsExample: AllegroGraph, InfoGrid, Neo4j
- 12. Amazon SimpleDBKey-value storeWritten in Erlang, (as is CouchDB)Data is modeled in terms ofDomain, a container of entities,Item, an entity and Attribute and Value, a property of an ItemEventually Consistent, except when ReadConsistent flag specifiedImpressive performance numbers, e.g., .7 sec to store 1 million recordsSQL-like SELECTselect output_listfrom domain_name[where expression] [sort_instructions] [limit limit]
- 13. Google DatastorePart of App Engine; also used for internal applicationsUsed for all storageIncorporates a transaction model to ensure high consistencyOptimistic lockingTransactions can failCAP implicationsDatastore isn’t just “eventually consistent”They offer two commercial options (with different prices)Master/Slave Low latency but also lower availabilityAsynchronous replicationHigh ReplicationStrong availability at the cost of higher latency
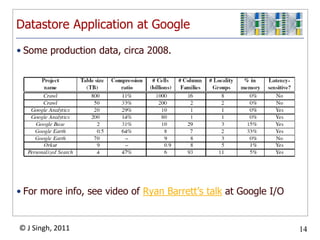
- 14. Some production data, circa 2008.
- 15. For more info, see video of Ryan Barrett’s talk at Google I/ODatastore Application at Google
- 16. Databases and Key-Value Storeshttp://browsertoolkit.com/fault-tolerance.png
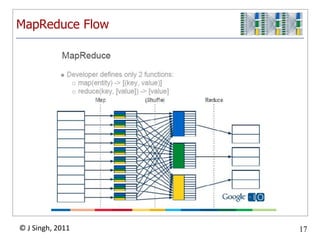
- 17. MapReduce Conceptual UnderpinningsProgramming model from Lisp and other functional languages(map square '(1 2 3 4)) (1 4 9 16)(reduce + '(1 4 9 16)) 30 Easy to distributeNice failure/retry semantics
- 18. MapReduce Flow
- 19. HadoopMapReduceAn Open Source project of the Apache FoundationOther Hadoop-related projects at Apache include:Cassandra™: A scalable multi-master database with no single points of failure.HBase™: A scalable, distributed database that supports structured data storage for large tables.Hive™: A data warehouse infrastructure that provides data summarization and ad hoc querying.Pig™: A high-level data-flow language and execution framework for parallel computation.See the Apache Hadoop website for more.
- 20. Hadoop AvailabilityRun on your laptopRun on your serverRun on Amazon CloudIntroduction at IBM DeveloperWorksRun on Google App EngineIt’s not Hadoop, it’s Google’s implementation of MapReduce
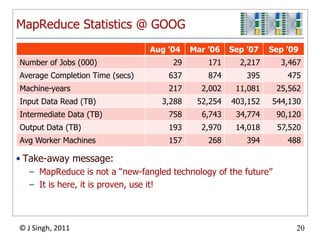
- 21. MapReduce Statistics @ GOOGTake-away message:MapReduce is not a “new-fangled technology of the future”It is here, it is proven, use it!
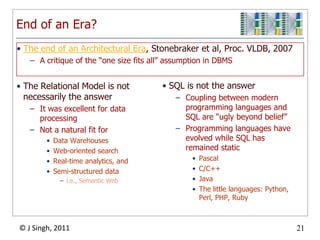
- 22. End of an Era?The Relational Model is not necessarily the answerIt was excellent for data processingNot a natural fit forData WarehousesWeb-oriented searchReal-time analytics, andSemi-structured datai.e., Semantic WebSQL is not the answerCoupling between modern programming languages and SQL are “ugly beyond belief”Programming languages have evolved while SQL has remained staticPascalC/C++JavaThe little languages: Python, Perl, PHP, RubyThe end of an Architectural Era, Stonebraker et al, Proc. VLDB, 2007A critique of the “one size fits all” assumption in DBMS
- 23. Take AwaysNoSQL databases are a solution to web-scale problemsA lot of data lives outside relational databasesWith SQLnix.org, we are starting a local resource for NoSQL database knowledgeTaking on projects to apply the technology, not just read about it.If you want to work on it, please contact us.Thanks










![Amazon SimpleDBKey-value storeWritten in Erlang, (as is CouchDB)Data is modeled in terms ofDomain, a container of entities,Item, an entity and Attribute and Value, a property of an ItemEventually Consistent, except when ReadConsistent flag specifiedImpressive performance numbers, e.g., .7 sec to store 1 million recordsSQL-like SELECTselect output_listfrom domain_name[where expression] [sort_instructions] [limit limit]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nosql-110601101336-phpapp01/85/NoSQL-and-MapReduce-12-320.jpg)